как проверить производительность vps
Слова для поиска: бенчмарк, скорость, benchmark
Задача:
Как определить производительность сервера?
Решение:
Простой тест диска
Это довольно простой тест позволяющий оценить производительность системы хранения без установки дополнительных специальных утилит.
dd if=/dev/zero of=testfile bs=64k count=16k conv=fdatasync
Значение опций:
- if=/dev/zero - в качестве источника данных используется псевдо-устройство являющееся генератором нулей
- of=/test.bin - это файл куда записывается информация. Не забудьте после теста удалить этот файл
- bs=64k - размер блока данных 64 килобайта
- count=16k - количество блоков данных записываемых в файл. В итоге получается файл размером 1Гб.
- conv=fdatasync - физическая запись на диск для исключения влияния кэширования записи
После выполнения команды будет выведена информация о скорости выполнения.
dd if=/dev/zero of=testfile bs=64k count=16k conv=fdatasync 16384+0 записей считано 16384+0 записей написано скопировано 1073741824 байта (1,1 GB), 9,30189 c, 115 MB/c
Затем можно оценить скорость чтения:
echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches #очистить кэш dd if=testfile of=/dev/null bs=64k 2097152+0 записей считано 2097152+0 записей написано скопировано 1073741824 байта (1,1 GB), 1,12647 c, 953 MB/c
Здесь команда dd прочитает файл testfile и запишет его в псевдо-устройство /dev/null. Устройство /dev/null это нечто вроде системного шредера или черной дыры для уничтожения всего, что туда попадает.
Простой тест сети
vvvvv
Измерение общей производительности
Установите утилиты time make file gcc
yum install time make file gcc или для debian | ubuntu apt-get install time make file gcc
Возможно потребуется еще
yum install perl-Time-HiRes
или
apt-get install libtime-hires-perl
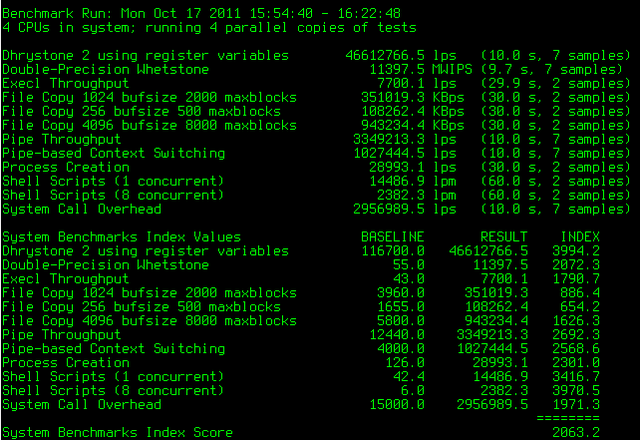
Скачайте утилиту по ссылке unixbench , распакуйте и запустите.
wget http://byte-unixbench.googlecode.com/files/UnixBench5.1.3.tgz tar -xzf UnixBench5.1.3.tgz cd UnixBench ./Run
Если одновременно запустить тест на множестве виртуальных серверов, то конечно результат будет далек от реально достижимого.
Подробности о Unixbench
UnixBench состоит из нескольких отдельных тестов, которые ориентированы на конкретные параметры.
Dhrystone
Этот тест используется для измерения и сравнения производительности компьютеров. Тест фокусируется на обработке строк. Результат во многом зависит от аппаратного и программного обеспечения, опций компилятора и компоновщика, оптимизации кода, кэш-памяти, состояния типов данных.
Whetstone
Этот тест измеряет скорость и эффективность операций с плавающей запятой. Используется широкий спектр функций, включая C SIN, COS, SQRT, математические операции, массивы обращений, условные переходы и вызовы процедур.
Execl Throughput
Этот тест измеряет количество execl вызовов в секунду. Execl является частью семейства функций Exec, выполняющих замену текущего образ процесса с новым.
File Copy
Измеряет скорость переноса данных из одного файла в другой с различными размерами буфера за 10 секунд.
Pipe Throughput
Измерение простейшей формы коммуникации между процессами. Измеряет сколько раз в секунду можно записать 512 байт в пайп и прочитать из пайпа.
Pipe-based Context Switching
Этот тест измеряет количество обменов данными через пайп между двумя процессами при котором тестовая программа порождает дочерний процесс, с которым оно осуществляет двунаправленный обмен.
Process Creation
Измерение скорости создания блоков управления и распределения памяти для новых процессов. Результат сильно зависит от пропускной способности памяти.
Shell Scripts
Измерение количество раз в минуту процесс может начаться и обрабатывать набор из одного, двух, четырех и восьми одновременных копий скриптов.
System Call Overhead
Тест оценивает накладные расходы на выполнение системных вызовов.
Графический тест
Тест измеряет 2D и 3D производительность обработки графики. Эти тесты дают очень приблизительное представление о 2D-и 3D-производительности системы и будет зависеть не только от оборудования, но от того какие используются драйверы. Для графических тестов потребуется установка 3dinfo.
Запуск Unixbench
Синтаксис:
Run [ -q | -v ] [-i <n> ] [-c <n> [-c <n> ...]] [test...]
The option flags are:
- q Run in quiet mode.
- v Run in verbose mode.
- i <count> Run <count> iterations for each test – slower tests
use <count> / 3, but at least 1. Defaults to 10 (3 for
slow tests). -c <n> Run <n> copies of each test in parallel.
The -c option can be given multiple times; for example:
./Run -c 1 -c 4
will run a single-streamed pass, then a 4-streamed pass. Note that some tests (currently the graphics tests) will only run in a single-streamed pass. The remaining non-flag arguments are taken to be the names of tests to run. The default is to run “index”. See “Tests” below.
Tests
The available tests are organised into categories; when generating index scores (see “The BYTE Index” below) the results for each category are produced separately. The categories are:
system The original Unix system tests (not all are actually
in the index)
2d 2D graphics tests (not all are actually in the index)
3d 3D graphics tests
misc Various non-indexed tests
The following individual tests are available:
system: dhry2reg Dhrystone 2 using register variables whetstone-double Double-Precision Whetstone syscall System Call Overhead pipe Pipe Throughput context1 Pipe-based Context Switching spawn Process Creation execl Execl Throughput fstime-w File Write 1024 bufsize 2000 maxblocks fstime-r File Read 1024 bufsize 2000 maxblocks fstime File Copy 1024 bufsize 2000 maxblocks fsbuffer-w File Write 256 bufsize 500 maxblocks fsbuffer-r File Read 256 bufsize 500 maxblocks fsbuffer File Copy 256 bufsize 500 maxblocks fsdisk-w File Write 4096 bufsize 8000 maxblocks fsdisk-r File Read 4096 bufsize 8000 maxblocks fsdisk File Copy 4096 bufsize 8000 maxblocks shell1 Shell Scripts (1 concurrent) (runs "looper 60 multi.sh 1") shell8 Shell Scripts (8 concurrent) (runs "looper 60 multi.sh 8") shell16 Shell Scripts (8 concurrent) (runs "looper 60 multi.sh 16") 2d: 2d-rects 2D graphics: rectangles 2d-lines 2D graphics: lines 2d-circle 2D graphics: circles 2d-ellipse 2D graphics: ellipses 2d-shapes 2D graphics: polygons 2d-aashapes 2D graphics: aa polygons 2d-polys 2D graphics: complex polygons 2d-text 2D graphics: text 2d-blit 2D graphics: images and blits 2d-window 2D graphics: windows
3d: ubgears 3D graphics: gears
misc:
C C Compiler Throughput ("looper 60 $cCompiler cctest.c")
arithoh Arithoh (huh?)
short Arithmetic Test (short) (this is arith.c configured for
"short" variables; ditto for the ones below)
int Arithmetic Test (int)
long Arithmetic Test (long)
float Arithmetic Test (float)
double Arithmetic Test (double)
dc Dc: sqrt(2) to 99 decimal places (runs
"looper 30 dc < dc.dat", using your system's copy of "dc")
hanoi Recursion Test -- Tower of Hanoi
grep Grep for a string in a large file, using your system's
copy of "grep"
sysexec Exercise fork() and exec().
The following pseudo-test names are aliases for combinations of other tests:
arithmetic Runs arithoh, short, int, long, float, double,
and whetstone-double
dhry Alias for dhry2reg
dhrystone Alias for dhry2reg
whets Alias for whetstone-double
whetstone Alias for whetstone-double
load Runs shell1, shell8, and shell16
misc Runs C, dc, and hanoi
speed Runs the arithmetic and system groups
oldsystem Runs execl, fstime, fsbuffer, fsdisk, pipe, context1,
spawn, and syscall
system Runs oldsystem plus shell1, shell8, and shell16
fs Runs fstime-w, fstime-r, fstime, fsbuffer-w,
fsbuffer-r, fsbuffer, fsdisk-w, fsdisk-r, and fsdisk
shell Runs shell1, shell8, and shell16
index Runs the tests which constitute the official index:
the oldsystem group, plus dhry2reg, whetstone-double,
shell1, and shell8
See "The BYTE Index" below for more information.
graphics Runs the tests which constitute the graphics index:
2d-rects, 2d-ellipse, 2d-aashapes, 2d-text, 2d-blit,
2d-window, and ubgears
gindex Runs the index and graphics groups, to generate both
sets of index results
all Runs all tests
fio -name iops_read64k_20 --rw=randrw --bs=4k -iodepth 64 -directory=/var/tmp/ --size=2g -ioengine libaio --direct=1
Ссылки:
Актуальность: 2011/10/12 11:03